FPV Drone Types: Everything You Need to Know
First Person View (FPV) drones have revolutionized the aerial experience, allowing pilots to immerse themselves in real-time video transmission. This creates an unparalleled sense of presence and control, making you feel like you’re soaring through the skies. However, entering this field can be intimidating. With various drone types and technical jargon, knowing where to start can feel overwhelming. This guide covers the main types of FPV drones, their unique features, and answers to common questions.
1. Micro and Indoor FPV Drones
Ideal for beginners and those seeking thrills indoors or in small outdoor areas, micro and indoor FPV drones are a perfect starting point. These drones are characterized by their small size, lightweight design, and ability to agilely navigate tight spaces.
1.1 Tinywhoops
What is a Tinywhoop?
Tinywhoops are quintessential indoor FPV drones. They are incredibly small (typically with propeller sizes of 65-75mm) and weigh under 30 grams. Their compact size makes them excellent for weaving through tight spaces and performing agile maneuvers. Tinywhoops usually feature ducted propellers (hence the “whoop” name). These ducts make them safer for indoor flying by protecting the propellers from impacts and reducing the risk of damage to surroundings or injury. Popular models include the Emax Tinyhawk and BetaFPV Meteor series.
Can you fly Tinywhoops outdoors?
Yes, you can fly Tinywhoops outdoors, but their small motors and light frames make them susceptible to wind and weather conditions. Calm days with minimal wind are ideal for outdoor Tinywhoop flights.

1.2 Micro/Nano FPV Drones
Micro and nano FPV drones are designed for indoor and close-range flying. They provide an accessible entry point into the FPV world due to their affordability and ease of use.
Do micro drones exist?
Yes, micro drones absolutely exist. In the FPV community, “micro drones” and “nano drones” refer to drones larger than Tinywhoops but still smaller than typical outdoor racing or cinematic drones. They are usually defined by frame sizes between 75mm and 150mm, weigh under 250 grams (avoiding FAA registration in the US), and use 1S–2S batteries.
How high can micro drones fly?
Due to limited battery life, micro drones typically have a maximum range of 50-100 meters and signal range.
What’s the difference between mini and micro drones?
Mini drones typically have frame sizes of 150mm to 250mm, while micro drones range from 75mm to 150mm. Minis are more powerful and versatile, whereas micros are ideal for indoor flying.
Are nano drones real?
Yes, nano drones are real. “Nano drones” generally refer to the smallest category with frame sizes under 75mm, perfect for indoor flying, often synonymous with Tinywhoops or even smaller innovations pushing the boundaries of miniaturization.
How far can nano drones fly?
Nano drones generally have a limited range of 50-150 meters due to battery and signal output constraints.
What’s the difference between micro and nano drones?
While both terms denote very small drones, “nano drones” usually imply something smaller than “micro drones.” Micro drones are larger and more powerful, offering longer flight times and ranges. Nano drones prioritize portability and are limited to very short ranges.

1.3 Toothpick Drones
What is a toothpick drone? Toothpick drones bridge the gap between indoor micros and outdoor-capable drones. They are named for their ultra-light frames, typically built around thin carbon fiber “toothpick” arms. These drones prioritize minimal weight for maximum agility and efficiency, suitable for both indoor and outdoor flying.
2. Cinematic FPV Drones
Cinematic FPV drones are designed to capture smooth, high-quality aerial video and photos. They prioritize stability, payload capacity (for better cameras), and smooth flight characteristics over raw speed or extreme agility.
2.1 Cinewhoops
What does Cinewhoop mean?
“Cinewhoop” is a portmanteau of “cinematic” and “whoop.” It describes an FPV drone type that adopts the ducted propeller design of Tinywhoops but in a larger, more powerful format. The ducts enhance safety and durability while allowing agile, cinematic flights in tighter environments.
Which Cinewhoop is the best?
The “best” Cinewhoop depends on your specific needs and budget, but here are some popular and highly regarded options, categorized by common use cases:
For GoPro/Action Cam Cinewhoops (versatile and popular):
- DJI Avata: A highly integrated and user-friendly option from DJI, known for its ease of use, excellent video quality, and safety features. Ideal for cinematic FPV beginners.
- iFlight CineBee/CineRace: Popular pre-built options for performance, durability, and value.
- GEPRC Cinebot/CineLog: Another reputable brand’s cinematic whoops.
How fast are Cinewhoops?
Cinewhoops typically fly at 30-60 km/h (18-37 mph), prioritizing stability over speed.

2.2 Cinelifters
What is a cinelifter?
Cinelifters are the “heavy artillery” of cinematic FPV drones. These are large, powerful multirotor drones designed to carry professional cinematic cameras, such as DSLRs, mirrorless cameras, or even small cinema cameras, for high-end aerial filmmaking.
What’s the difference between Cinewhoop and Cinelifter?
The main differences lie in size, payload capacity, and intended camera use:
- Cinewhoops: Like agile cinematic sports cars—versatile, fun, and capable of capturing great shots in many scenarios.
- Cinelifters: Like heavy-duty professional camera cranes in the sky—built to carry the biggest and best cameras for top-tier cinematic quality in demanding productions.
3. Racing and Freestyle FPV Drones
This category includes FPV drones designed for high-speed racing, acrobatic freestyle maneuvers, and long-range exploration. These prioritize performance, durability, and range over cinematic smoothness.
3.1 Racing Drones
What is FPV racing?
FPV racing is a competitive sport where pilots wear FPV goggles to navigate purpose-built racing drones through complex, obstacle-filled courses. The goal is to complete the course as quickly and accurately as possible. It’s a high-skill, high-adrenaline activity combining drone piloting, reaction times, and strategic route navigation.
Which drones are used for racing?
Popular FPV racing drones include the EMAX Hawk Pro, TBS Vendetta, and custom 5-inch quads optimized for speed.
How much do racing drones cost?
Racing drones typically range from $200 to $800, depending on components, frame materials, and customizations.
Are racing drones legal?
Racing drones are legal in most areas, but pilots must comply with local aviation regulations, including frequency usage and visual line-of-sight rules.
How fast can racing drones go?
High-performance racing drones can reach speeds of 160 km/h (99 mph) or more.
How far can racing drones fly?
While speed is the focus, racing drones need adequate range to cover tracks. Typical racing range: 300 meters – 1 km (1000 feet – 0.6 miles) is usually sufficient for race courses. Racing drones can be configured for longer ranges, but this is often secondary to speed and agility.
What’s the difference between freestyle and racing FPV?
FPV racing and FPV freestyle are distinct but related FPV disciplines:
- FPV Racing: Like Formula 1 or MotoGP—high-speed, technical, competitive, focused on lap times and winning on the track.
- FPV Freestyle: Like skateboarding or snowboarding—about personal style, creativity, performing tricks, and expressing yourself through aerial maneuvers.
3.2 Freestyle Drones
What is FPV freestyle?
FPV freestyle is a form of FPV flying focused on aerial performances, tricks, and creative maneuvers in open spaces or urban environments. It’s about self-expression, pushing the limits of drone agility, and capturing visually stunning freestyle flight videos.
How fast is FPV freestyle?
Freestyle drones can reach 100-120 km/h (62-74 mph), but prioritize maneuverability over raw speed.
What size drone is best for freestyle?
5-inch drones are the standard for freestyle due to their balance of power, control, and durability.
What’s the best FPV freestyle drone?
Like Cinewhoops, the “best” freestyle drone is subjective, depending on pilot preferences and budget. Favorites in FPV freestyle include the iFlight Nazgul5, GEPRC Mark5, and custom 5-inch quads.
3.3 Long-Range Drones
Long-range FPV drones are optimized for distance, ideal for exploration, surveying, and mountain surfing.
What’s the best size for long-range FPV?
7-inch drones for their efficiency and stability.
What’s the maximum FPV range?
FPV’s “maximum range” is continually pushed by advancements in technology and adventurous pilots. However, practical and legal limits exist:
- Practical long-range (reliable signal): With optimized setups and good conditions, pilots can reliably achieve 5-10+ km (3-6+ miles), or even farther.
- Extreme range records: Record-breaking long-range flights in controlled environments can reach 50+ km (30+ miles) or more with specialized equipment.
Which FPV drone has the longest range? There’s no single “longest-range FPV drone” model, as long-range FPV is often about custom builds and optimized components. Drones designed for long-range typically feature:
- Larger frames (6-7 inches+): For efficiency and battery capacity.
- Efficient motors and props: Optimized for long flight times.
- High-capacity batteries: Li-Ion batteries for energy density.
- Long-range radio systems: Such as TBS Crossfire, FrSky R9, or ELRS (ExpressLRS), known for extended range capabilities. GPS and Return-to-Home (RTH): Essential safety features for long-range flights.
Is long-range FPV legal?
It depends on local laws. In the US, FAA requires Visual Line of Sight (VLOS), making ultra-long-range illegal without waivers.
Conclusion
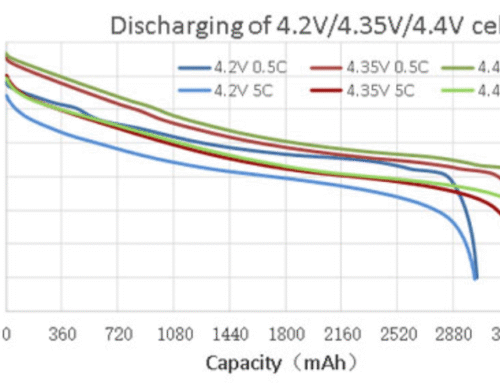
FPV drones offer a wide range of possibilities, from indoor exploration to high-speed racing and professional cinematography. Understanding the differences between various FPV drone types ensures you select the best platform for your needs while adhering to legal and safety standards. Newbettercell is a leading manufacturers provide a variety of FPV batteries tailored for different FPV drones, from Tinywhoops to racing quads. Battery capacities range from 270mAh to 9000mAh, with discharge rates (C ratings) from 15C to 250C, meeting specific application requirements.